Application of Infrared Technology in Carbon Dioxide Detection and Research
Carbon dioxide is one of the major factors causing global climate change. The detection, capture, treatment of carbon dioxide, and the development of carbon dioxide detectors have become one of the main directions of scientific research in the 21st century. Optimizing the energy structure and improving the efficiency of energy use are the main methods for the rational use of energy, the development of energy, and energy conservation and emission reduction. However, currently some of the fuel resources, especially petroleum and coal, have not been fully utilized in the combustion process, and some of the resources are wasted in the intermediate links. Therefore, the detection of energy use efficiency is a prerequisite for understanding the efficiency of energy-saving films and improving the utilization efficiency. Carbon dioxide detection and residual carbon analysis of petroleum, coal-burned gas, and post-combustion dust can calculate the efficiency of combustion. In order to achieve carbon dioxide emissions and the governance of the atmosphere.
Application:
Package
Decorative film for furniture
Christmas tree leaves
Features:
Matte or glossy and even embossed for added visual impact
Ideal for UV offset, screen, inkjet digital and flexographic printing,
Easily to be folded, bended, cut, thermoformed, welded, glued and coated.
Specification:
Size: variable, customized
Surface: matt, glossy
Color: transparent, translucent, opaque, colored (white, red, yellow, black, etc.)
Pvc Film For Printing,Printable Pvc Film,Printed Pvc Film,Pvc Printed Film Y&YTRA , https://www.pvcprod.com
1 On-line detection of carbon dioxide The detection of carbon dioxide in the environment requires that the detection method must be online, so that real-time data in the environment can be obtained in a timely manner, and a rapid response to changes in environmental parameters can be made and measures taken as soon as possible. The use of infrared technology to detect carbon dioxide content is one of the main means to achieve online measurement.
1.1 Principle of Infrared Absorption Gas Sensor The infrared absorption plow carbon dioxide gas sensor is based on the principle that the absorption spectrum of gas varies depending on the substance. The chemical structure of different gas molecules is different, and the absorption of different wavelengths of infrared radiation is different. Therefore, when infrared radiation of different wavelengths sequentially illuminates the Sword-like substance, certain wavelengths of radiation energy are selectively absorbed and weakened by the sample substance, resulting in an infrared absorption spectrum. Therefore, when the infrared absorption spectrum of a certain substance is known, it can be obtained from The absorption peak of this substance in the infrared region was obtained. When the same substance has different concentrations, there is a different absorption intensity at the same absorption peak position, and the absorption intensity is proportional to the concentration. That is, different gas molecules have different chemical structures and correspond to different absorption spectra. Each gas, in its spectrum, has strong absorption of light of a specific wavelength. By detecting the effect of gas on the wave K and intensity of light.
1.2 sensor design Infrared carbon dioxide sensor probe structure shown in Figure l. It is from infrared light source, measurement 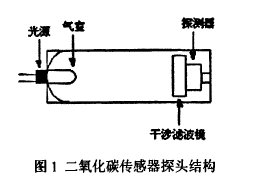 Gas chamber, adjustable interference filter, optical detector, light modulation circuit, amplification system and other components. Non-measured components in the air, such as methane, carbon monoxide, and water vapor, affect the measurement results. The infrared filter has a wavelength of 4.26 um, and carbon dioxide has a strong absorption at this wavelength; carbon monoxide and methane and other gases do not absorb it. Therefore, the interference of carbon monoxide and methane is negligible; however, water vapor interferes with the determination of carbon dioxide, which can reduce the reflectivity of the air chamber, and thus reduce the sensitivity of the instrument and affect the accuracy of the measurement result. Therefore, the air sample must be dried. After that, enter the instrument again. In the air chamber, carbon dioxide absorbs the light emitted by the light source at a specific wavelength, and detection by the detector can show the absorption of infrared light by carbon dioxide. The interference filter is adjustable and it can be adjusted so that it can change the wavelength of light that it passes through, thereby changing the strength of the signal detected by the detector. The infrared detector is a film capacitor. After absorbing the infrared energy, the temperature of the gas increases, causing the pressure in the air chamber to increase. The distance between the two electrodes of the capacitor will change, and the capacitance value will change accordingly. The greater the concentration of C02 gas, the greater the change in capacitance.
Gas chamber, adjustable interference filter, optical detector, light modulation circuit, amplification system and other components. Non-measured components in the air, such as methane, carbon monoxide, and water vapor, affect the measurement results. The infrared filter has a wavelength of 4.26 um, and carbon dioxide has a strong absorption at this wavelength; carbon monoxide and methane and other gases do not absorb it. Therefore, the interference of carbon monoxide and methane is negligible; however, water vapor interferes with the determination of carbon dioxide, which can reduce the reflectivity of the air chamber, and thus reduce the sensitivity of the instrument and affect the accuracy of the measurement result. Therefore, the air sample must be dried. After that, enter the instrument again. In the air chamber, carbon dioxide absorbs the light emitted by the light source at a specific wavelength, and detection by the detector can show the absorption of infrared light by carbon dioxide. The interference filter is adjustable and it can be adjusted so that it can change the wavelength of light that it passes through, thereby changing the strength of the signal detected by the detector. The infrared detector is a film capacitor. After absorbing the infrared energy, the temperature of the gas increases, causing the pressure in the air chamber to increase. The distance between the two electrodes of the capacitor will change, and the capacitance value will change accordingly. The greater the concentration of C02 gas, the greater the change in capacitance.
The block diagram of the detection circuit design is shown in Figure 2. The detection circuit consists of an infrared carbon dioxide sensor, a digital filter circuit, an amplifying circuit, a steady current circuit, a single-chip microcomputer system, and the like. The basic principle of the design is that the infrared carbon dioxide sensor converts the detected carbon dioxide gas concentration into a corresponding electrical signal, and the output electrical signal is respectively filtered, amplified, input to a single-chip microcomputer system, and processed by temperature and pressure compensation, etc. The system outputs the display device to display its measured value. 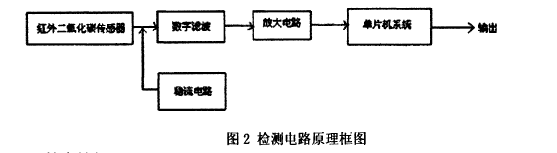
1.3 Technical Performance Infrared absorption carbon dioxide sensor is based on the principle that the gas absorption spectrum varies with different substances. It integrates the filter processing, with temperature compensation, amplification and other circuits, the carbon dioxide concentration or volume fraction is converted into a voltage signal, and output after release. The sensor has the advantages of compact structure, simple structure, small size, high precision, good selectivity, low temperature coefficient, convenient installation and carrying, and can be widely used for real-time remote monitoring and control of carbon dioxide in environment monitoring and various harsh environments.
2 Residual Carbon Detection of Dust Collect the powder remaining after burning or the dust in the air. Detecting the organic carbon content in the dust can understand the nature of the dust and have a better understanding of the environmental conditions. For combustion systems, the combustion efficiency of mountain burning equipment can be calculated.
2.1 Principles of detection Residual carbon analysis refers to the principle of residual carbon analysis in petroleum exploration. After analysis of rock samples, the total organic carbon content of the rock sample can be calculated. The principle of detection is to pass air into the sample. After the sample is fully oxidized at a temperature of 600° C., the concentration of C02 produced is measured. The chemical reaction can be expressed as:
C+02→C02
According to the integral processing of real-time concentration data n(t), the corresponding residual carbon content is converted accordingly 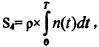 Where p is the conversion factor.
Where p is the conversion factor.
2.2 Instrument Design Figure 3 shows the design principle of the residual carbon analyzer. The instrument is mainly controlled by a single-chip microcomputer, and a high-precision temperature control of the heating furnace is realized by temperature detection and output voltage regulation. An infrared sensor and a peripheral acquisition circuit are used to achieve on-line collection of carbon dioxide concentration, and the flow is detected by the flow detection and valve control circuit. Automatic control. In addition, through the connection with the computer, the later data processing is completed by the computer to obtain accurate residual carbon data. 
2.3 Technical Specifications Residual carbon detection uses a high-precision control system to ensure that the temperature control accuracy is ±1°C and the flow control is up to 2%FS, which ensures the consistency of dust collection. The residual carbon analysis of dust takes into account the automatic collection of dust, and at the same time, the carbon content of dust and powder can be accurately measured after the sample is fully oxidized.
3 Application in petroleum exploration Although this scheme has not yet been formally applied to the analysis of environmental monitoring and residual carbon in combustibles, residual carbon analysis of substances has been successfully applied to the petroleum exploration industry. In the oil exploration, it mainly analyzes the content of hydrocarbon compounds in various rock samples. The study of the content of hydrocarbons can effectively calculate and measure the nature of each stratum in the earth's surface, the gas's gas reserves, and the quality of oil and gas. By performing residual carbon analysis on the rock samples from each rock below the ground, the total organic carbon content of the sample can be calculated. Through the analysis of total organic carbon content, it is also possible to calculate the oil generation potential of the oil rock of birth, and play a crucial role in the evaluation of the lithology, oil and gas quality, and oil and gas content of the ground-F rock layer. In order to achieve the purpose of oil exploration and discovery oil and gas reservoirs. Through the analysis of the national standard sample, when the sample is 100 mg, the residual carbon value at 2 mg/g can fully guarantee the accuracy and linearity of the analysis.
Infrared carbon dioxide detection can effectively perform downhole carbon dioxide gas formation  Identification and evaluation, according to the relationship between carbon dioxide and the surrounding environment (lithology, porosity, etc.) determine the gas interpretation results. Residual carbon analysis technology can effectively evaluate the oil production ability of downhole oilstones, and determine the type and oil level of the horizons by combining residual carbon data with other exploration methods (pyrolysis analysis, chromatographic analysis, gas analysis, etc.). And other information. Through years of on-site exploration, infrared carbon dioxide detection technology has been successfully applied in petroleum exploration.
Identification and evaluation, according to the relationship between carbon dioxide and the surrounding environment (lithology, porosity, etc.) determine the gas interpretation results. Residual carbon analysis technology can effectively evaluate the oil production ability of downhole oilstones, and determine the type and oil level of the horizons by combining residual carbon data with other exploration methods (pyrolysis analysis, chromatographic analysis, gas analysis, etc.). And other information. Through years of on-site exploration, infrared carbon dioxide detection technology has been successfully applied in petroleum exploration.
4 Oil and coal combustion system quality monitoring program design For the quality monitoring of petroleum and coal combustion systems, a carbon dioxide sensor can be used to achieve both on-line monitoring of carbon dioxide and residual carbon detection of combustion dust. The multiplexing of sensors is realized, which greatly reduces the detection cost and results in more detection parameters.
The scheme is to introduce the exhaust gas emitted by burning into the carbon dioxide detector through the sample pump, and then collect and record the real-time data by a computer or a data acquisition instrument. A gas filtration device is installed in front of the sample pump to collect the dust particles of the sampled gas. The instrument then analyzes the dust and calculates the residual carbon content of the dust. Figure 4: 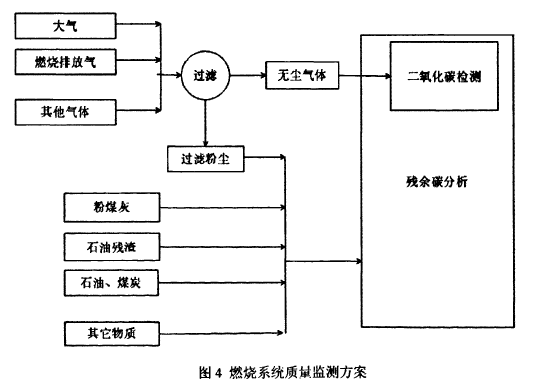
In the actual production process. The total organic carbon (TOC) content in the unit of combustion can be obtained by the TOC analysis of the combustion itself. The concentration of the emitted exhaust gas is collected in real time in production to obtain the real-time collection concentration C ( %). The residual carbon content RC (me/g) under different combustion conditions (opening, feeding, etc.) or the residue of the burned petroleum residue or coal residual carbon value RC' (mg/g) is obtained by residual carbon analysis. The combustion efficiency of the combustion system can be measured by the relationship between the organic carbon content A and the residual carbon value RC or RC':
n = RC/Ax 100% - Combustion efficiency under different combustion conditions n' = RC'/Ax 100% - Combustion efficiency during the entire combustion process can also be summarized based on the real-time carbon dioxide concentration and the residual carbon value at the time The relationship between the concentration C and the combustion efficiency 礓 is n=f(C), and the combustion efficiency data is correlated with the carbon dioxide data. Realize the real-time detection of combustion efficiency, so as to achieve timely detection and timely treatment, improve combustion efficiency, and reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
5 Conclusions Carbon dioxide on-line detection and dust residue carbon analysis using infrared technology can be applied not only to the detection of the efficiency of the combustion system, but also to the monitoring of the atmospheric environment in living areas, industrial parks and other areas. It is also possible to add more detection elements (such as carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitric oxide gas detection elements) on the basis of the program to achieve more comprehensive environmental index monitoring. The program is based on years of oil exploration and analysis technology derived from the environmental testing program, despite a lot of work, but still need to be perfect and pending the test of practice. It is hoped that the vast numbers of experts and scholars will give us more guidance and help. Through everyone's efforts to better detect the combustion system's combustion efficiency, to achieve carbon dioxide emissions.